Diagnosis of heart disease with CT scan
Diagnosis of heart disease with CT scan
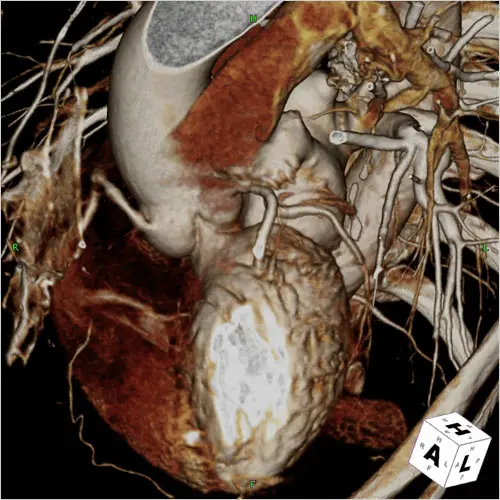
Computer tomography, commonly known as CT scans, combines several X-ray images with the help of a computer to create cross-sectional views of the body. Cardiac CT is a cardiac imaging technique that uses CT technology with or without intravenous contrast material injections to visualize the anatomy of the heart, circulation of large veins and vessels (including aorta, pulmonary veins and arteries). Diagnosis of heart disease by CT scan is a very effective and useful method.
How does a heart CT scan work?
Cardiac CT scan is a low-invasive or noninvasional process. Perhaps somehow it can be said that a CARDIAC CT scan is an outpatient examination and the scan itself takes about five minutes to complete.
In some cases, you may need contrast agents before a CT scan. Contrast paint is a liquid substance that contains iodine and helps structures such as blood vessels show up in clearer X-rays. You may receive contrast agents by drinking liquids or injecting orally.
During the CT of the heart, you will lie motionless on a flat, narrow bed attached to a cardiac CT scan. During the scan, which takes only a few minutes, you can communicate with the technician. The device rotates around you and takes X-rays from all different angles. A computer processes and combines these incisions to create detailed images of the blood vessels around your heart. The radiologist checks the images and sends a report to your doctor.
Why should we do a CT scan?
Cardiac CT scans provide valuable information to your doctor. CT scans are more detailed than conventional radiology. Using 3D computer images, doctors can pinpoint blood clots, infections, tumors and other issues surrounding coronary arteries. This information can help your doctor determine the causes of chest pain and other symptoms. Your doctor can then control and guide treatment for a range of cardiovascular diseases.
Your doctor may prescribe a CARDIAC CT scan to check for certain conditions. These conditions can include:
- Congenital heart disease or congenital heart defect
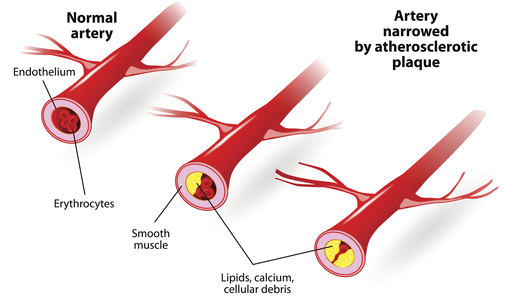
- Accumulation of a hard substance called lipid plaque that may block your coronary arteries
- Defects or damage to the four main heart valves
- Blood clots in the heart cavities
- Tumors inside or on the heart
Cardiac CT scan is a common imaging technique for people experiencing heart problems. The reason for the CARDIAC CT scan is because it allows your doctor to check the structure of your heart and adjacent blood vessels without making any incisions.
A variety of CT scan methods are used to diagnose heart disease, including:
- Calcium Screening Heart Scan
- Coronary Artery CT Angiography (CTA)
- Whole body CT scan
Calcium Screening Heart Scan
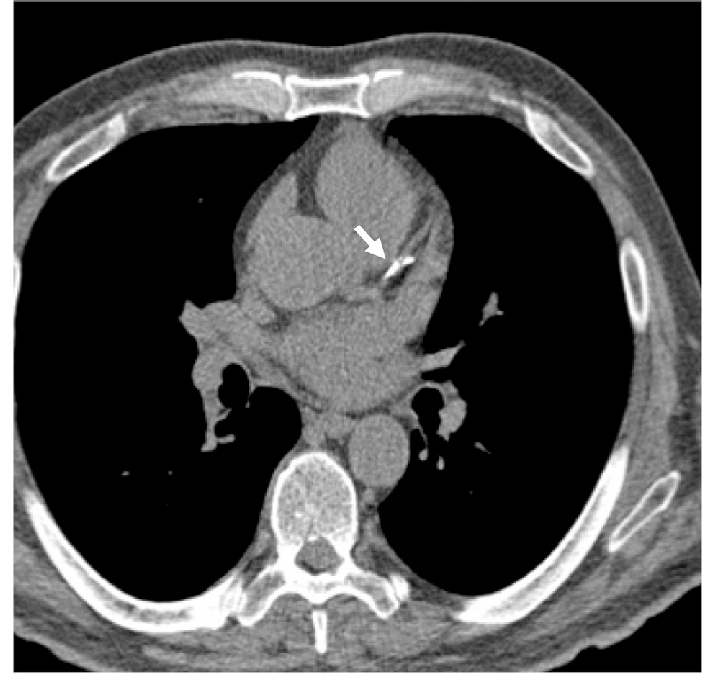
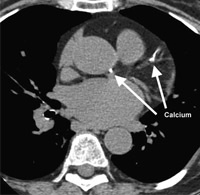
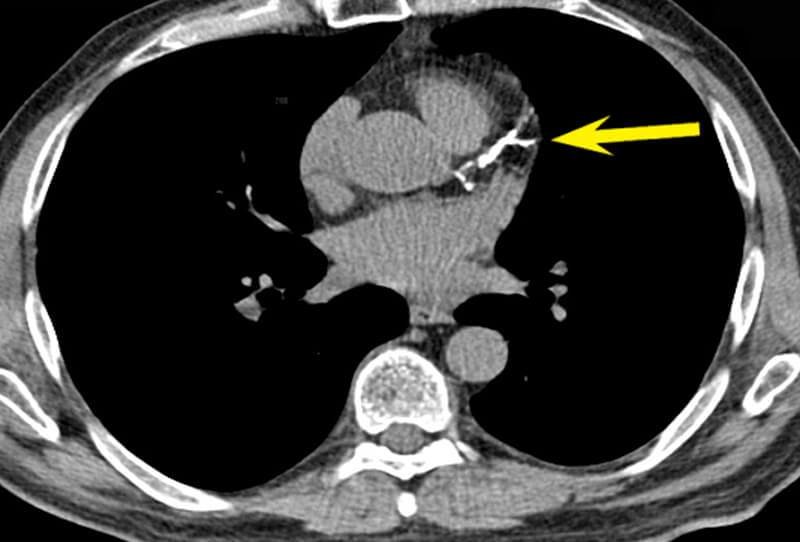
Cardiac scan is an experimental calcium score screening that is used to detect calcium deposits in atherosclerotic plaque in coronary arteries. Modern computerized tomography methods, such as cardiac scans, are the most effective way to early detection of coronary artery calcification caused by atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), before the symptoms of this fatal disease emerge. Coronary calcium intake is known as an independent and powerful predictor method for future heart problems and is useful in making lifestyle changes and guiding preventive care to reduce their risk.
Your doctor will use a heart screening scan with a calcium score to assess the risk of heart disease. If calcium is deposited in the vessels, the computer creates a calcium “rating” that estimates the rate of coronary artery disease based on the number and density of calcified coronary plaques in the coronary arteries.
Lack of calcium is considered a “negative” test. However, since there are certain types of coronary artery disease such as atherosclerosis of “soft plaque” that are not diagnosed in heart CT scans, it is important to remember that negative testing indicates a low risk, but does not absolutely rule out the likelihood of developing the disease. So if your heart CT scan was written negatively, be happy, but note that the risk of a heart attack is still not zero.
Heart screening with a calcium score takes only a few minutes and does not require intravenous iodine injections.
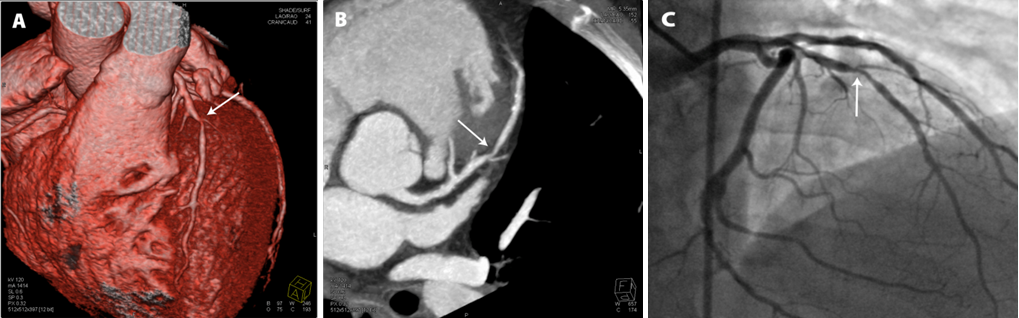
Cardiac CT Angiography (CTA)
Cardiac CT Angiography (CTA) is a noninvasive cardiac imaging technique that is currently rapidly developing and progressing. 3D and high-resolution images of the mobile heart and large vessels are produced during cardiac CT angiography to determine whether fat or calcium deposits (plaque) were created in the coronary arteries.
Before cardiac CT angiography, a colored substance containing iodine is injected into the vein in the patient’s arm to improve the quality of the images. A drug that slows or stabilizes a patient’s heart rate may also be given through a trazy to improve imaging results.
During cardiac angiocyte CT, which usually lasts about 10 minutes, X-rays pass through the body and are captured by special detectors in the CT scanner. Newer CT scanners create more transparent final images with lower X-ray doses (which is much better for the patient’s health) than older models. These new technologies are often referred to as “multi-detector” or “multi-slice” CT scans.
Since cardiac CT angiography is a non-invasive procedure, it can lead to lower risk and discomfort for patients much faster than cardiac catheterization (also called cardiac catheter (also called cardiac catheter or cardiac angiography).
Although the use of cardiac CT angiography examinations is on the rise, coronary angiography remains the “gold standard” for diagnosing coronary artery stenosis, which is a significant artery stenosis that can require catheter-based intervention (such as stenting) or surgery (such as bypass).
Cardiac CT angio is useful for determining whether symptoms of chest pain may be caused by a blockage of the heart vessels, especially in people who may be at risk, such as those with a family history of heart events, diabetes, high blood pressure, smokers or those with high cholesterol levels. However, there are still disagreements among experts about when cardiac CT angiography should be used.
What is the difference between cardiac CT scan and cardiac angiocardio?
Cardiac CT scans and angiography are similar ways to create images of your blood vessels. However, there are differences between cardiac CT scan and cardiac angio CT scan. Traditional angiography is a more invasive process that uses a catheter or cardiac spring to the coronary arteries to deliver contrast paint. Angiography can also combine diagnosis and treatment in one way. On the other hand, cardiac CT scan is a non-invasive procedure that produces only images and is not considered a therapeutic method.
Interpretation of cardiac CT scan response
The cardiac CT scan answer is usually given numerically called the Agatstone score . The score reflects the total level of calcium deposits and calcium density.
A score of zero means no calcium in the heart. This score indicates a low likelihood of developing a heart attack in the future.
When calcium is there, the higher the score, the higher the risk of heart disease.
A score of 100 to 300 means moderate plaque deposition. This score is associated with a relatively high risk of heart attack or other heart disease over the next three to five years.
A score of more than 300 is a sign of a very high to severe disease risk and a heart attack.
You may also see a percentage score in your heart CT scan that shows your calcium levels compared to people of the same age and gender.
Keep in mind in general that the outcome of a heart scan should not be used as a predictor of your overall health and heart disease risk. Information from heart scans should be combined with other patient health information.
You can be informed of many medical imaging methods in medical scans. For example, in a medical scan, you can find out more about cardiac CT scans. More importantly, in a medical scan, you can take a CARDIAC CT scan and get your CT scan answer online.
Cardiac CT scan can
be performed in medical scans in all cities of the country.