Types of ultrasound – What are the types of ultrasound imaging applications and different ultrasound scans?
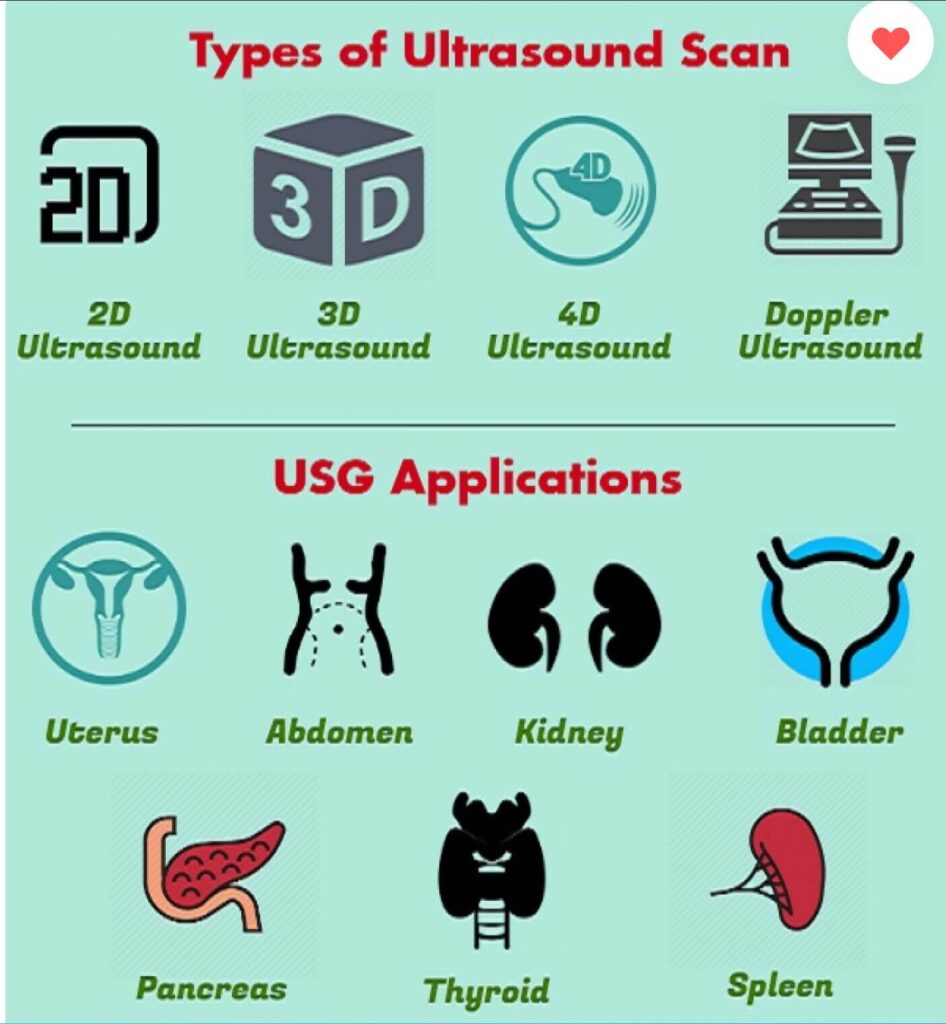
Types of ultrasound
Ultrasound is one of the most widely used methods of medical imaging today and it can be said that the most common type of medical imaging in the world is ultrasound. But ultrasound has different methods for different organs. So in this article, we are going to familiarize you with the types of ultrasound that are performed in imaging centers and answer the question of what are the types of ultrasound imaging applications and different ultrasound scans?
So we go to different organs and explain the application of ultrasound in each of these organs. So stay with the medical scan .
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a useful method for evaluation of internal organs such as liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and bladder. This scan can help diagnose a variety of conditions and assess the damage caused by various diseases. Since ultrasound shoots organs in real-time, it can also be used for:
Procedures such as needle biopsies, in which needles are used to sample organ tissue cells for laboratory tests.
Abdominal ossography helps doctors determine the origin of many abdominal pains, such as stones in the gallbladder or kidney. It also helps identify the cause of enlarged abdominal organs.
Doppler ultrasound is a special type of ultrasound scan that examines the main blood vessels and arteries. Doppler ultrasound output images can help your doctor see the following phenomena:
• Blockage of blood flow, such as blood clots
• Plaque build-up inside the vein
• Congenital anomalies
Pelvic Ultrasound
Pelvic ultrasound is one of the most well-known types of ultrasound. This scan is one of the imaging tests used to monitor the health of the fetus during pregnancy. In addition to examining the health of the fetus, this type of ultrasound is also used to examine the uterus, ovaries, bladder and prostate gland.
Pelvic ultrasound is often used to diagnose the condition or causes of these conditions, including:
- Pelvic pain
- Abnormal bleeding
- Menstrual problems
- Ovarian cysts
- Uterine fibroids
- Ovarian and uterine cancer
- Kidney stones and bladder
Transvaginal or intrauterine ultrasound
In transvaginal ultrasound, the woman’s patient must drain her bladder in the same way. He also lay upwards on his back. The ultrasound transducer or probe must enter the patient’s uterus for this test. This probe usually has a smaller diameter and size than other ultrasound probes. A protective coating and gel for lubrication are placed on the probe before inserting it into the vagina.
Only the first two to three inches of the transducer are placed in the vagina. The doctor may move the probe around during the scan to obtain images from different angles. The most common reason for transvaginal pelvic ultrasound is searching for the cause of pelvic pain.
Intraoral or trans rectal ultrasound
For ultrasound on the prostate gland, the ultrasound probe must be inserted through the rectum (anus) so that sound waves can reach the prostate and have echoes. Like other conventional ultrasound methods, the probe is first coated with a protective coating before being inserted into the anus and lubricated with a special ultrasound gel. The converter must be moved to obtain images from different angles. These examinations are usually performed by lying on the left side and bending the knees towards the chest.
If you see a lesion during the examination, your doctor may recommend a biopsy. In the biopsy, the radiologist uses ultrasound images to direct a needle towards the prostate gland and extract a sample of abnormal tissue. Ultrasound-guided biopsies are low-invasive and only require a small incision.
Obstetrics and Gynecology Ultrasound
Ob ultrasound refers to the specialized use of ultrasound for imaging and thus determining the status of a pregnant woman and her fetus. Obstetrics and gynecology ultrasound should be performed only if needed clinically and only by order. Some of the signs and symptoms that may persuade your doctor to prescribe an ultrasound for obstetrics and gynecology include:
- Determining the viability of the fetus
- To estimate the age of pregnancy
- For diagnosis of congenital malformations
- To assess the position of the fetus
- To evaluate the position of the placenta
- To determine whether there is multiple pregnancy
To perform this scan, the mother is asked to lie on her back or side. The patient is also asked to expose your underbelly area. The obstetrics and gynecology ultrasound examination takes about 30-45 minutes.
This scan is a painless procedure. You may feel mild pressure on your abdomen as your doctor will direct the transducer on your abdomen, especially if you need to have a full bladder to perform a scan. At times, the sonographer may have to push the probe a little harder to get closer to the fetus to better visualize the physical structure of the fetus. But don’t worry at all because it’s temporary pain and discomfort. Also, you may not like the feeling of a water-soluble gel on your abdomen. With transvaginal scans, there may be minimal discomfort with the movement of the transducer in the vagina.
Ultrasound of the arterial carotid system and abdominal aorta
Ultrasound of the arterial carotid system is a rapid and noninvasive means of detecting blood flow blockage in the cervical arteries to the brain, which may lead to stroke. Abdominal aortic ultrasound is primarily used to evaluate an aneurysm, which abnormal enlargement of the aorta is usually caused by atherosclerotic disease.
For carotid ultrasound and abdominal aorta, the patient will first be placed on the bed of the ultrasound device. Then, a transparent gel is applied to the area to be examined. The gel helps the transducer to make safe contact and eliminates air holes between the transducer and the skin, as sound waves cannot penetrate the air. The sonographer or radiologist then presses the transducer firmly on the skin and moves along the desired area, checks the images on the monitor and takes “snapshots” if necessary.
Liver Ultrasound
Liver ultrasound determines the size, shape and function of the liver and can be used to diagnose tumors.
Kidney Ultrasound
Ultrasound determines the size, shape and function of the kidneys and can be useful in the diagnosis of kidney stones, cysts and tumors.
Vascular Ultrasound
Vascular ultrasound is used to analyze blood flow through arteries and veins.
Thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound examines hypoactive and hyperactive thyroid glands, nodules and cysts.
Final word:
We hope that the article on the types of ultrasound from the scan of medicine will be useful for you and we have briefly introduced the different types of
ultrasound
that we have already explained about each one. For ultrasound, you can get your
ultrasound
through the medical scanning platform and its appointment system to identify the best ultrasound centers around you through the
imaging centers
page of the Scan Teb website and get your turn from these centers.