Nuclear Medicine
About Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear Medicine is a branch of medical science in which radioactive materials are used to diagnose and treat diseases. Diagnostic methods apply to different organs such as bones, brain, kidney, lung, heart, gastrointestinal tract, etc.
Nuclear medicine imaging is one of the most key and basic imaging methods to understand the biological properties and functions of body tissues. This type of imaging is performed by injecting a substance called nuclear drug (radiopharmaceptic). The nuclear drug allows the placement and measurement of biochemical processes in the body using radiomedics.
These include evaluating organ function, such as heart, kidney, liver, thyroid, etc. is. It also facilitates the location, measurement and analysis of the activity of some cancers. The information obtained from this type of imaging is completely different from anatomical imaging methods such as CT-Scan or MRI.
Imaging method in nuclear medicine is such that first radiopharmaceuticals for each organ are marked with radioactive substance and injected to the patient and accumulate in the organ. Then, the organ is imaging using a gamma-gamma device.
Unlike radiology methods that generally provide information about organ building, nuclear medicine methods generally provide nuclear medicine specialists with information about the function of different organs.
Types of devices used in the nuclear medicine sector
In general, this can be divided into the equipment and devices used in the nuclear medicine sector. It can be divided into two general parts: main devices and nuclear medicine accessories.
The main nuclear medicine devices can be divided into cyclotron, pet-MRI, pet-CT, spect-CT, spect, gamma-camra, bone densitometration and treadmill measurement and for all capital devices there is UPS.
The accessories used in the nuclear medicine sector are as follows:
– Doscalibrator
– Paravan Sareli
– Lead gown
– Lead buckets for waste or radioactive waste
– Lead shield for syringe handling
– Lead shield for transporting vials
– Lead glasses
– Thermometer and humidifier for use in the installation room of nuclear medicine devices
– Badj Movie
– And the rest of the office supplies for use in the reception section
It should be noted that nuclear medicine centers may have some of these items in the center depending on the services they provide.
Services provided in the nuclear medicine sector:
In the nuclear medicine department, due to its application in the diagnosis of diseases, the following services are provided:
Heart scan or heart nuclear scan
Nuclear heart scans are useful in diagnosis and evaluation of coronary artery disease. It is also used to evaluate cardiomyopathy and identify possible damage to the heart due to chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Doctors use heart nuclear medicine scans to help diagnose heart disease. These heart diseases include:
- Unexplained chest pain
- Chest pain caused by exercise (called angina).
- Shortness of breath
- Electrocardiogram (abnormal electrocardiogram 9)
Nuclear heart scans are also performed for other purposes, including:
- To visualize blood flow patterns in the heart walls, that is called myocardial perfusion scan.
- To assess the presence and extent of suspected or known coronary artery disease.
- To determine the extent of damage to the heart after a heart attack or myocardial infarction.
- To evaluate the outcomes of bypass surgery or other vascular reconstruction procedures designed to restore blood supply to the heart.
- Along with electrocardiogram (ECG), to evaluate the movement of the heart wall and overall heart function with a technique called Gated Cardiac.
Some imaging centers combine nuclear medicine images with CT scans or MRI to create special views. Doctors call this image fusion. Merging these images allows the doctor to view information from two different imaging in a connected image. This leads to more accurate information and more accurate diagnosis.
Finally, it can be said that heart nuclear medicine scans provide images of blood flow distribution in the heart muscle and can be used to identify abnormal blood flow in the heart, determine the extent of heart muscle damage after a heart attack or measure and evaluate heart function.
Bone scan
A whole body bone scan is a special type of nuclear medicine that uses small amounts of radioactive materials to detect and assess the severity of a variety of bone diseases and conditions, including fractures, infections and bone cancer.
Since nuclear medicine methods are capable of imaging body functions at the molecular level, they offer the potential to identify the disease at an early stage as well as the patient’s response to therapeutic interventions. In fact, bone scans can often find bone abnormalities much earlier than a typical X-ray scan.
In general, nuclear bone scans are used to assess any changes in bones such as osteoarthritis in the joints, finding bone diseases and tumors, or determining the cause of bone pain or inflammation.
Gallium scan
Gallium scans are used to diagnose active infectious or inflammatory diseases, tumors and abscesses. In general, gallium scans can help diagnose the following disorders:
Cancer, like Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
infections, such as abscesses (pus collectors) or osteomyelitis (bone infections).
Inflammatory conditions (e.g., pulmonary fibrosis or sarcoidosis).
Gallium scans are often used when a person has a fever for an unknown reason. Also, often after treatment, the doctor may look for the remaining cancer cells in the patient’s body to further check the patient’s health using gallium scans.
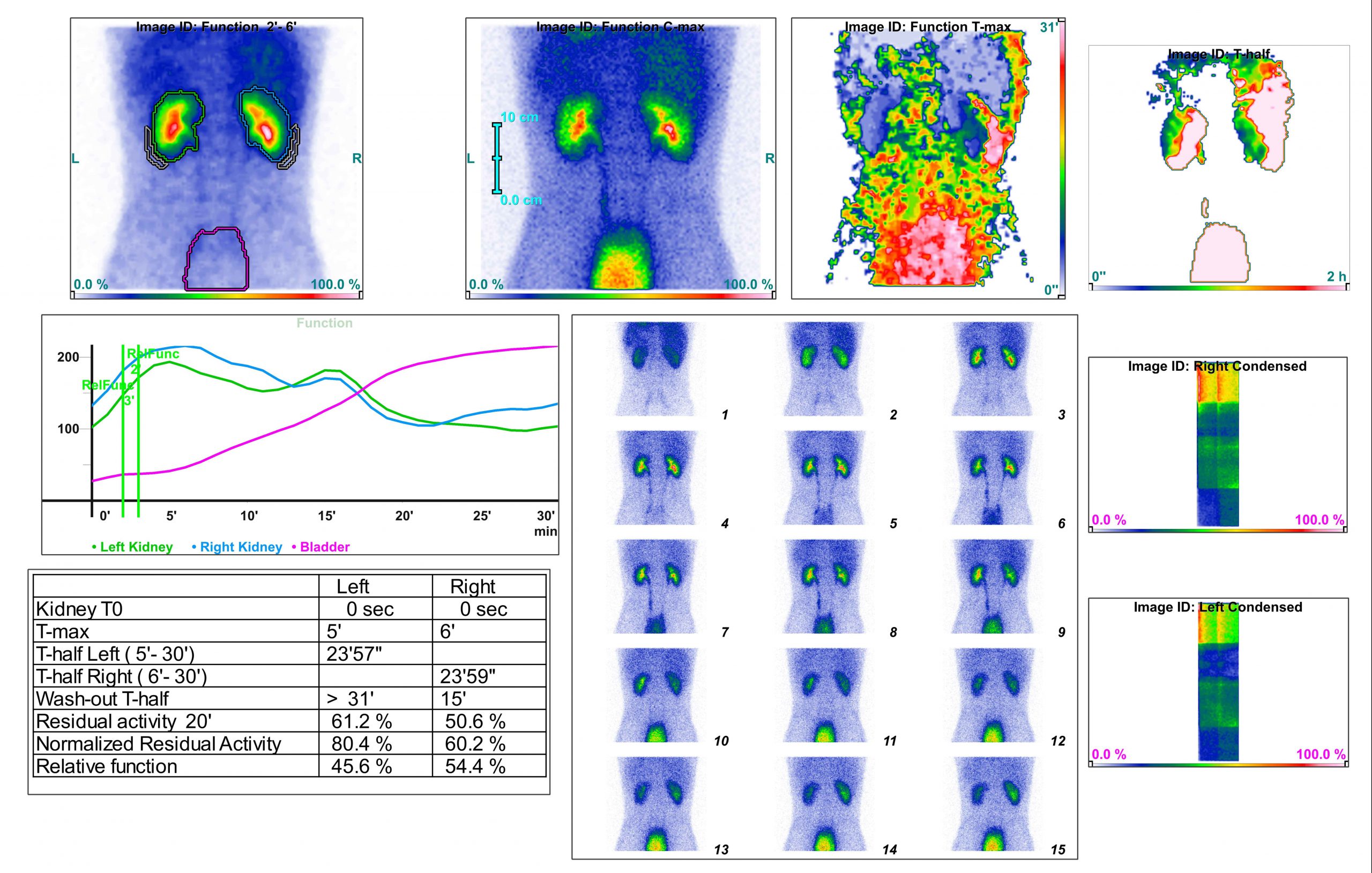
Kidney scan by nuclear medicine or kidney nuclear scan
Kidney nuclear scans are used to check the kidneys and find any abnormalities in the kidneys and ducts of the adrad. These abnormalities mainly involve abnormal functioning or obstruction of renal blood flow. A nuclear scan shows all how the patient’s kidneys work.
Nuclear brain scan
A nuclear brain scan or, more precisely, a brain perfusion scan is a nuclear medicine scan that examines blood flow in different areas of the patient’s brain. Brain perfusion scans can be used to diagnose various diseases, including dementia, stroke, ischemia and in some forms of epilepsy.
Areas of the brain that are very active often show more blood supply as well as more oxygen and glucose consumption. Tracking these increases can show which areas of the patient’s brain are more active. These factors may be lower in areas of the brain that are damaged or not very active.
If your doctor has prescribed you a brain nuclear scan, it may be for one of the following reasons:
- Epilepsy
- Dementia
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack
- Sub-spider bleeding
- Carotid stenity
- Cerebral vasculitis
- Brain tumor
- Head injury
In general, brain nuclear scans are used to investigate problems within the brain or in circulation to the brain.
Nuclear breast or breast scan
Breast nuclear scan is an imaging test for viewing breasts. Breast nuclear scans are often used when mammography has not given enough information to the doctor. Areas of the breast where radiopharmaceps are accumulated in larger quantities are called “hot spots”.
Areas that don’t absorb the tracker and look less bright in the scanned image are called “cold spots.” Cancer cells are usually hot spots in breast scans.
Breast scans can be useful in diagnosing breast cancer in young women. Young women usually have denser breasts than older women. Dense breast tissue may also occur due to:
- Fibrocystic disease
- Breast adipose tissue
- Breast surgery in the past
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Biopsy
- Breast Implants
Your doctor may prescribe a breast nuclear medicine scan if one of the following conditions is likely:
- Tumor
- Infection (abscess)
- Blood collection called hematoma
- Cyst
Doctors may also use a breast nuclear scan to check blood flow in breast tissue.
If a patient has breast cancer, a breast nuclear scan can help diagnose the stage of cancer. Doctors may also use this scan as follow-up after surgery, chemotherapy or other breast cancer treatments. In general, breast nuclear scans are often used along with mammography to determine the location of cancerous tissue in the breast.
Nuclear thyroid scan
The thyroid helps maintain many different functions of the body by processing and regulating levels of certain hormones. A nuclear thyroid scan is performed to allow doctors to determine which parts of the thyroid gland are functioning properly and whether the thyroid gland is hyperactive (hyperthyroidism) or underperforming (hypothyroidism).
It may also help differentiate between benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) thyroid nodules. Thyroid scans also give information about the size and shape of the thyroid gland. In general, thyroid nuclear scans are used to evaluate thyroid function or to better evaluate nodule or thyroid mass.
Other nuclear medicine scans such as:
Liver and spleen scans
Tear duct scan
Gastrointestinal scan and RBC
Nuclear gallbladder and bile duct scans, lung nuclear scans, urinary tract scans and parathyroid nuclear scans are also available that you can read on the medical scan platform and get these scans through medical scans.
Positronic Diffusion Journalism (PET)
A imaging technique is nuclear medicine, which gives a 3D image or a picture of the process of functioning within the body. The system reveals a pair of gamma rays produced by a positron radionuclide (tracer) and emitted in opposite directions.
This radionuclide is inserted into the body by an active biological molecule. Then, the 3D image of the density of the drug inside the body is reconstructed by computer analysis. In new scanners, a CT scan is usually taken simultaneously on the same device to make the 3D image more accurate.
In this method, the patient’s body is injected with a specific chemical marked with a radioactive substance (radiopharmaceno). Different tissues of the body absorb different amounts of this substance according to their blood flow and cellular and chemical metabolism. This absorbed material itself emits an unoroted beam that can be received by a special imaging device.
Principles of Pet Scan Function in Nuclear Medicine
According to the above introduction, pet imaging principles can be considered based on the detection of inorganic radiation resulting from the destruction of positron and electron pairs, so radioisotopes used in PET are C11, N13, O15 and F18 which have half-life of 20, 10, 2 and 110 minutes, respectively.
If the biological molecule activated for PET imaging (FDG) is F18 (a glucose compound), the obtained image shows the metabolic activity of the tissue in areas where glucose uptake is high. This substance is a marked derivative of glucose that is very low and in general and normal conditions there is no significant risk of using this technology.
The most common type of PET scan, about 95% of current scans in standard medical care, is the use of FDG to look for the possibility of cancer metastasis.
PET scan is a non-invasive imaging technique in nuclear medicine that is used in diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of various diseases and widely used in clinical oncology (medical imaging of tumors and searching for metastasis) and clinical research of brain diseases such as dementia and also in cancer, cardiovascular and neurological diseases.
Some other common uses of PET include oncology, neurology, cardiology, pharmacology, small animal imaging, muscle-bone imaging and cancer diseases, especially gastrointestinal, breast and lemfoam cancers.
Pet Scan Benefits
In most failures and diseases, changes in metabolism occur before anatomical changes occur in the tissue, so unlike conventional imaging systems, MRI and CT, which measure anatomical or SPECT changes that measure physiological changes.
Using the PET system, we are able to diagnose the disease at an early stage and prevent the progression of the disease and treat it, and as we know about cancer, early diagnosis is vital for treatment.
If we want to compare the PET system with the SPECT system, which is now the most common system in the nuclear medicine sectors, the following should be taken into consideration:
1- The separation power of pet system, which is the ability of the system to represent the components of the organ studied in the image, is about 4 to 5 mm, which is twice as good as the SPECT separation power.
2- PET efficiency is much better than SPECT system, which makes the images more clear and contrastable
3- Due to the possibility of correction for radiation absorption in PET, quantitative analysis of information is possible which has many applications in determining the stage of the disease.
4- PET in nuclear medicine, in addition to the possibility of studying the physiological process of tissue or organ studied, there is the possibility of studying the metabolism and biochemistry activity of the studied tissue, which is the most prominent advantage of this system which distinguishes it from other imaging systems.
In order to get the fastest turn of nuclear scan or nuclear medicine, take the nuclear turn of the medical scan.
You can also visit the CDC website if you need more detailed information about nuclear medicine.