Ultrasound centers and 17 of their imaging services
Ultrasound centers are definitely the most frequent medical imaging centers. This indicates the importance and application of ultrasound in the field of medicine. Each ultrasound center provides a list of services to individuals. In this paper, we are going to describe the ultrasound centers and 17 imaging services separately. So stay with us for enough information.
1- Pregnancy ultrasound
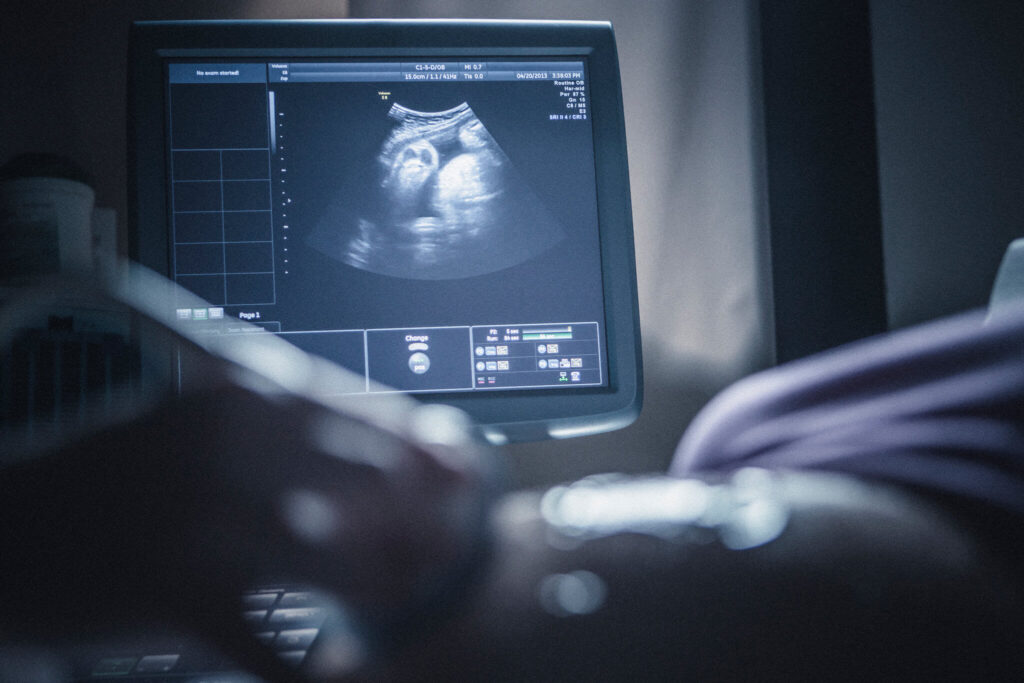
Most pregnant women usually receive only two ultrasounds, one at the beginning of pregnancy and the other in the middle of pregnancy. Other women may perform three or more strains depending on several factors. Sono pregnancy is usually done for a number of reasons, mainly for:
• To confirm (make sure) being pregnant
• To check the child’s age and development – this will help your doctor determine the date of delivery.
• To check your heart rate, muscle tone, movement and overall growth of the child
• To check if you are pregnant with twins, triplets or more (also called multiples)
• To check if your child is in the first position of the head before birth
• For examination of the ovary and uterus (uterus). The ovaries are where the eggs are stored in the body.
• The doctor also uses ultrasound for screening and other tests. Screening means seeing if your child is more likely to develop a disease than others. This does not mean making sure your child is infected.
• For screening of congenital defects, such as spina bifida or heart defects. After an ultrasound, your doctor may want to do more tests, called diagnostic tests, to make sure your baby has a congenital defect. Congenital defects are conditions that the baby experiences at birth. Congenital defects change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body. These congenital defects can cause problems in overall health, how the body grows, or how the body functions.
• To help with other prenatal tests, such as biopsies of chorionic villus (also called CVS) or amniocentesis. CVS is when placenta cells are taken for testing. Placenta is a tissue that provides nutrients for your baby. Amnio is an experiment in which amniotic fluid and cells are taken from the bag around your baby.
• To assess pregnancy complications, including ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy and miscarriage.
• Determining the gender of the fetus
2- Doppler Ultrasound
Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive test that can be used to estimate blood flow through your blood vessels by irradiating high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) into circulating red blood cells. A typical ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images, but it can’t show blood flow.
Doppler ultrasound may help diagnose many diseases, including:
• Blood clots
• Weak valves in the veins of your leg, which can cause blood or other fluids to accumulate in your legs (venous insufficiency)
• Heart valve defects and congenital heart disease
• Artery blockage
• Decreased circulation in the legs (peripheral artery disease)
• Vascular bulge (aneurysm)
• Narrowing of an artery, such as your cervical artery (carotid artery stenification)
Doppler ultrasound can estimate blood flow rate by measuring the rate of change in step (frequency). During Doppler’s ultrasound, a technician trained in ultrasound imaging presses a small handheld device (transducer) the size of a piece of soap on your skin in the examined area of the body and starts moving from one area.
This scan may be performed as an alternative to more invasive procedures, such as angiography. Doppler ultrasound tests may also help your doctor check for damage to your arteries or check for some treatments for your veins and arteries.
3- Uterine ultrasound
Uterine ultrasound is a noninvasive diagnostic test that produces images used to evaluate the organs and structures inside the female pelvis. Uterine ultrasound enables rapid visualization of female organs and pelvic structures, including the uterus, cervix, vagina, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
4- Breast and armpit ultrasound
Breast and armpit ultrasounds are often performed to check if a problem with mammography or physical breast examination may be a cyst filled with fluid or a solid tumor. Breast ultrasound is not usually performed for breast cancer screening. This is because it may lose some of the early signs of cancer. A sample of early signs that may not appear in ultrasound are small calcium deposits called microcalcifications.
Ultrasound centers that have linear or flat probes perform this ultrasound, you can get breast ultrasound from different centers through a scan of the medicine.
Ultrasound may be used in the following cases:
• Breast tissue is particularly dense so that mammography may not be able to see the tissue.
• The possibility of pregnancy
• For ages under 25
Your doctor may also use ultrasound to check the adjacent lymph nodes, help guide the needle during a biopsy or remove fluid from the cyst.
5- Fetal Ultrasound
Fetal ultrasound is an imaging technique that uses sound waves to produce images of the fetus in the uterus. Fetal ultrasound images can help your doctor evaluate the development of your fetus and monitor your pregnancy. In some cases, fetal ultrasound is used to assess possible problems or help confirm the diagnosis. The first fetal ultrasound is usually performed in the first trimester to confirm pregnancy and estimate the duration of pregnancy. If your pregnancy remains uncomplicated, the next ultrasound is usually provided during the second trimester, when anatomical details of the fetus are visible. If the fetus is suspected of having a problem, the next ultrasound or additional imaging tests such as MRI may be recommended.
There are two main types of fetal ultrasound:
Transvaginal ultrasound:
In this type of fetal ultrasound, a device called a transducer is placed in the vagina of pregnant mothers to send sound waves and collect reflections. Transvaginal ultrasound is often used in early pregnancy. This type of ultrasound may also be performed if trans-abdominal ultrasound does not provide sufficient information.
Trans-abdominal ultrasound:
Fetal ultrasound is performed through the abdomen by moving a transducer onto your abdomen.
Other types of ultrasound are available through the abdomen, including:
Specialized evaluation of ultrasound: This type of examination may be required in certain circumstances, such as when a fetal malformation is known or suspected. In these circumstances, a more detailed assessment can provide more information about anomalies.
3D Ultrasound: This type of ultrasound is sometimes used to help doctors diagnose facial abnormalities or nervous system defects.
Fetal Doppler ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound measures minor changes in ultrasound waves when they mutate from moving objects such as blood cells. Fetal Doppler ultrasound can provide details about the baby’s blood flow.
Fetal echocardiography: This scan provides a detailed picture of the baby’s heart. Fetal echocardiography may be used to confirm or rule out congenital heart defects.
6- Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound is performed in most ultrasound centers throughout the country. Pelvic abdominal ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure used to evaluate the organs and structures inside the abdomen. These organs include the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, bile ducts, spleen and abdominal aorta. Ultrasound technology enables rapid visualization of abdominal organs and structures from outside the body. Ultrasound may also be used to evaluate blood flow to the abdominal organs.
Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound may be used to assess the size and location of abdominal organs and structures. It can also be used to check the abdomen for conditions such as:
- Cysts
- Tumors
- Pus collection (abscess)
- Blockages
- Collecting liquids
- Blockage (clots) in blood vessels
- Infection
Abdominal aortic size can be measured by ultrasound to detect aortic aneurysm. The presence of stones in the gallbladder, kidneys and estuer may be diagnosed with ultrasound.Abdominal ultrasound may sometimes be performed to help insert needles used to biopsy abdominal tissue or drain fluid from cysts or abscesses. Abdominal ultrasound may also be used to evaluate the blood flow of various structures inside the abdomen.
7- Color Doppler ultrasound of arterial and venous vessels
Color doppler ultrasound of arterial and venous vessels is used to check blood flow in large arteries and veins of arms or legs. Doppler ultrasound checks blood flow in the main arteries and veins in the arms and legs using ultrasound.
8- Sonography of thyroid and endocrine glands
Thyroid ultrasound is an imaging method to see the thyroid, a gland in the neck that regulates metabolism. Thyroid and endocrine ultrasound is usually performed when a physical examination reveals any of these findings:
• There is an abnormal growth on your thyroid gland called thyroid nodules.
• A large or irregular thyroid is called goiter.
• You have abnormal lymph nodes near your thyroid.
Ultrasound is also often used to guide needles in biopsies of the following:
• Thyroid nodules or thyroid glands – In this test, a needle pulls a small amount of tissue out of the node or thyroid gland. This is a test for the diagnosis of thyroid disease or thyroid cancer.
• Parathyroid gland.
• Lymph nodes in the thyroid.
9- Bladder and urinary tract sonography
Bladder and urinary tract sonography uses sound waves to provide images of the bladder before and after urine. Doctors prescribe bladder ultrasound if they have concerns about bladder problems, such as difficulty urinating. Bladder ultrasound can show how much urine the bladder holds when filled and whether someone empties the bladder completely when they urinate. This can indicate whether there is anything unusual about the bladder, such as its size, thickness of bladder walls, obstruction or kidney stones. Bladder ultrasound is often performed along with kidney ultrasound.
10- Ultrasound caller doppler organs
Caller Doppler ultrasound can help diagnose blockages in the bloodstream to your various organs, as well as help diagnose conditions such as abdominal masses, gallbladder disease and gallstones, as well as problems with your liver, kidneys, pancreas or spleen.
11- Pediatric Ultrasound
Ultrasound scan is a non-invasive test that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce an image from inside the body. Ultrasound scans are painless and do not use X-rays, meaning it is very safe to shoot babies and children.
You can take a child ultrasound without problems from ultrasound centers across the country and go to the ultrasound centers without any problems through a medical scan and perform a pediatric ultrasound scan. So don’t worry about harming babies and children during ultrasound scans.
12- Transvaginal ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound is an experiment used to examine women’s uterus, ovaries, tubes, cervix and pelvic area. Transvaginal means vaginal or intravaginal. The ultrasound probe is inserted inside the vagina during testing. During transvaginal ultrasound, a doctor or medical technician inserts the transducer into the patient’s vagina while the patient is lying on your back on the examination table. The transducer emits sound waves that produce images of pelvic organs, including the ovaries.
13- Liver ultrasound of gallbladder pancreatic spleen
Abdominal ultrasound is a non-invasive procedure used to evaluate the organs and structures inside the abdomen. This ultrasound includes the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, bile ducts, spleen and abdominal aorta. Ultrasound technology enables rapid visualization of abdominal organs and structures from outside the body.
14- Ultrasound of the kidney of the prostate bladder
Prostate scans use sound waves to produce images of the male prostate, which can help detect symptoms such as blood transfusions or difficulty urinating. Kidney ultrasound scans may be used to assess the size, location and shape of the kidneys and related structures such as urs and bladder. Ultrasound scans can detect cysts, abscess tumors, stones, obstructive fluid buildup and infection in and around the kidneys. Bladder scans can be used to help identify bladder dilation. Bladder ultrasound can also identify the causes of frequent urination and irritability of the bladder.
Kidney and bladder scans are usually performed if you see any of the symptoms as follows:
- Urinary incarceration
- Increase frequent urination especially at night
- See blood in the urine and semen
- Feeling of not draining the bladder
15- Sonography of Children and Infants
Sonography provides a clear picture of soft tissues that are not well represented in X-ray images. Ultrasound is very useful for assessing abdominal, pelvic or testicular sac pain in children and infants.
16- Hip Sonography
Hip ultrasound is used to photograph patients’ buttocks in order to find abnormalities in the pelvis. This scan can be performed in infants from neonatal period to about 6 to 8 months of age. Conditions that may require hip ultrasound include, but are not limited to:
- An abnormality found through a physical examination of the baby’s pelvis
- Family history of hip dysplasia
- Breech delivery
17- Ultrasound of inguinal
Ultrasound of the inguinal to check the right and left groin area. In case of feelings of mass or pain or sensitivity, your doctor may prescribe an inguinal ultrasound. Ultrasound looks more at the muscles and soft tissues of this area of the body, but can also see blood vessels and blood flow. Common reasons for requiring groin ultrasound include mass assessment.
Final Word
Different
ultrasounds
are common in the field of medical imaging because ultrasound is inexpensive and safe. Therefore, for many people, it may happen at least once that they want to get
an ultrasound
appointment. However, there have always been challenges of scanning, especially ultrasound. We have found a way to solve this problem in medicine scans. You can take a free ultrasound through
a medical scan
and easily see the answer to your scan on your laptop or phone. So take your close ultrasound without worrying.