X-ray tube repair

A CT scan resembles a cavity or tube in the shape of a doughnut that rotates an X-ray around you 360 degrees. The data taken provides a detailed 3D view of the inside of your body.
X-ray tube definition:
The X-ray tube, also called the Roentgen tube, is an e-drained tube that generates X-rays by accelerating electrons at high speeds with a high voltage field and hitting them with a target, the anode plate.
What is X-ray tube function?
The X-ray tube is tasked with creating X-ray photons from electrical energy supplied by the X-ray generator. The X-ray beam creation process is highly inefficient, so that only 1% of electrical energy is converted into X-ray photons and the remaining 99% is converted into heat in the X-ray tube set and body.
X-ray tubes are generally designed to function properly under the harshest conditions. So that X-ray tubes for desktop systems do not need to be replaced during the lifetime of the system, the lifetime of the X-ray tube for systems on Earth is usually between 3 and 7 years. This is mainly determined by how it is used and maintained. Therefore, in this paper, we will review the scan of medicine on the main recommendations for optimal use of X-ray tube.
What are the types of X-ray tubes?
This section describes different types of X-ray tubes and three types of high voltage circuits:
Simple X-ray tube
A simple X-ray tube is composed of a filament (cathode) that produces thermal electrons, and an anode that produces X-rays when electrons collide, is fixed and vacuumed in a glass tube. Many of these tubes are relatively small and are used at voltages from 20 kV to 130 kV.
X-ray tube with beryllium window (Be)
Many Oxford Instruments X-ray tubes are equipped with beryllium X-ray windows for maximum flux transmission. Beryllium is a metal that has low density and low atomic mass, hence very low X-ray absorption, making beryllium a preferred option for X-ray tube windows where low energy transmission is desired.
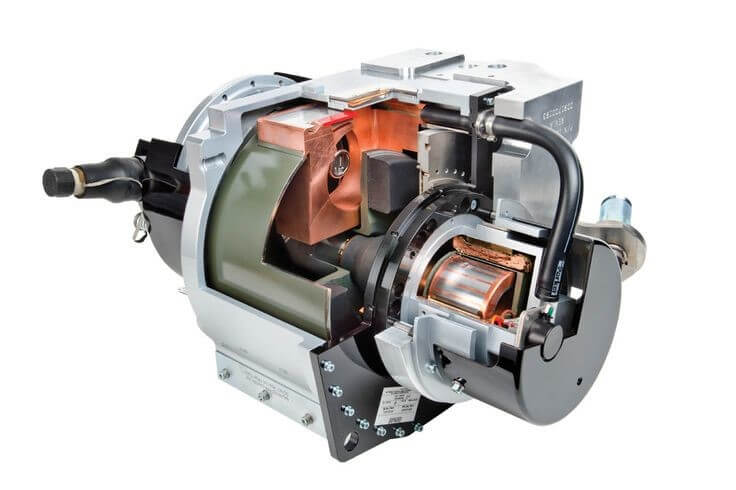
Rotating Anode X-ray Tube
A rotating anode is a small metal disc (usually tungsten or copper) that receives an electron beam from the cathode and emits it as an X-ray. The anode is placed at an angle that directs the X-ray beam towards the C arc, where the subject of the given scan is placed.
Ceramic X-ray tube
A metal ceramic X-ray tube, an X-ray tube with higher spatial resolution, better contrast, filtering and cooling, and a longer working life than conventional pipes are explained. The pipe has a steel outer jacket that is preserved in the earth’s potential. High voltage is applied directly to the anode and cathode.
End X-ray tubes or window X-ray tubes
X-ray tube with end window, a high flux tube is specifically designed for XRF applications and is used with a very thin window for light elements.
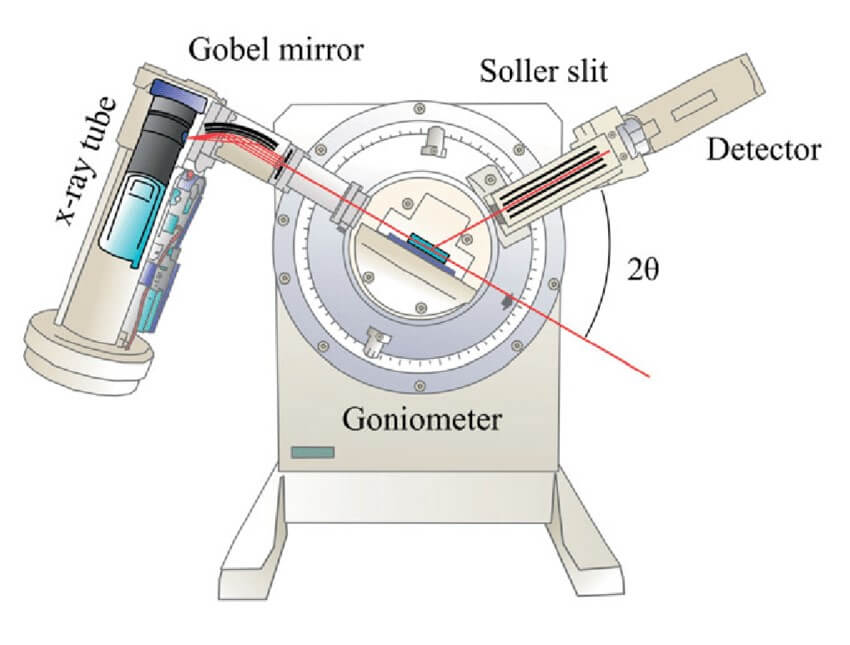
X-ray tubes for X-ray diffraction
These tubes are used in diffractometer or diffracometer. Diffraction Meter is a measuring instrument for analyzing the structure of a material of the dispersion pattern generated when beaming radiation with an X-ray tube.
Microfocus X-ray tube
What is microfocus X-ray tube?
Microfocus tubes have been used to improve image quality by providing the smallest focal point size and the possibility of increasing the magnification coefficient and thus increasing the visible resolution. Microfocus and Micro CT systems provide reliable resolution of up to 2 microns
Open X-ray tubes
The X-ray source of the open tube, as the name implies, is open. Open tube sources, which are generally composed of an all-metal structure, create a vacuum with a two-step pumping process each time the system is turned on from the cold. Vacuum is maintained throughout the system through a secondary pumping system.
- Maximum pipe voltage (kV): 80 to 150
- Agent: Sealed tube
- Main ownership costs: Replacement Pipes
- Maximum pipe power: 5-10 watts
What components does X-ray tube consist of?
The main components of the X-ray tube include cathode, anode, rotor, envelope, pipe port, cable socket and tube chamber.
How much do X-ray tubes cost?
The price of some tubes can be up to $700 or less, while the newest high-level systems may cost up to $100,000.
What is a modern X-ray tube?
Modern X-ray tube components 1. Cathode 2. Anode 3. Glass coating 4. Oil insulation 5. Pipe protector. 43. Cathode: • Has two main components: a) String b) CUP FILAMENT: • The source string of electrons inside the tube is X-ray. • Tungsten wire coil with diameter of about 2 mm and length of 1 cm or less.
General points in the maintenance of X-ray tubes
- Before checking the need to repair X-ray tubes, you need to know some preventive tips before repairing the tubes.
- X-ray tubes should not be left unused for a long time, in any case they should not be unused for more than 6 months. X-ray tubes like to be warm and this heat keeps the vacuum inside the tube stable.
- Use the Iso-Watt switching feature. This forces the spectrometer to operate at a constant power during the switch between different measurement conditions. A constant power contributes to the longevity of the X-ray tube.
- Use standby settings. On standby, the power – and especially the flow of emissions – shouldn’t be too high, as it costs a lifetime job. It’s ok to set the top of the kilolet on standby because it helps the tube stay stable against possible flashes.
- Keep the X-ray tube window clean. Make sure no material spills on the window and don’t touch the glass in any circumstances (even to clean the tube).
- Clean samples when analyzing compressed powders make sure they are well prepared and not crushed inside the spectrometer. Arranged sample preparation is an essential processing step for good analysis. This will help maintain the lifespan of your device’s tube.
Tips for keeping X-ray tube cooling and preventing X-ray tube repair
- Check chiller status regularly. Cooling water is vital (chemical and physical composition, temperature, flow), because the X-ray tube is heated, and this heat must be cooled by heat exchanger or chiller or tube cooling system, especially when it works at full power.
- The ideal water temperature for X-ray tubes is 20-25 °C. In extremely hot and humid conditions, temperatures of 30-25 °C are recommended. It’s better.
- One-handed and uninterrupted flow of cooling water is as important as the cooling water itself. Therefore, the cooling circuit of the pipe should be checked and cleaned regularly. If you experience an unusual reduction in tube temperature, be almost certain that the X-ray tube has not cooled properly and this problem may be from the tube cooling system.
- Never use pure ionized water to cool, as it is acidic and chemically invasive.
- In cool air imaging devices, put the cooler gap in the correct way, so that the tube in this cooled air mode reaches it faster.
Tips on X-ray tube settings
- When a CT scan or radiology device is not used for more than a few hours, it is best to put the tube on standby. This saves the lifespan of the tube.
- When the X-ray generator device is not used for more than 24 hours, turn off the X-ray tube completely.
- In X-ray generator systems that cool with water flow and so-called cooling water systems, when the X-ray tube is completely turned off, cut off the water flow within 2-1 minutes. Never allow water to flow more than 2 minutes after power is cut off. Otherwise, water condensation inside the X-ray pipe protector may occur.
- Never cut off the water flow first (by creating an automatic blackout), as it can instantly destroy the X-ray tube.
Tips to increase the stability and longevity of X-ray tubes
Each X-ray tube is designed to work at its maximum power. It is absolutely okay to use maximum power. However, it cannot be denied that any X-ray tube and KEL scan tube will cause physical and chemical aging. These aging processes are mainly driven by high temperatures and high temperature gradients inside CT scan tubes or X-rays.
At maximum power, the physical and chemical aging processes inside the X-ray tube are performed faster than less power.
Performance in 80-90% of maximum power currently has a significant positive effect on the stability and longevity of X-ray tube and CT tube.
If you unexpectedly need an X-ray tube or CT scan or X-ray tube repair, please contact Scanteb.
Teb Scan as the first medical imaging platform in the country can advise you on repairing X-ray tubes and CT scans and leave repairs to us.